:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Daryl-Sabara-Meghan-Trainor-Lead-208a72e9ce6e47b9827900d6b61ebd91.jpg)
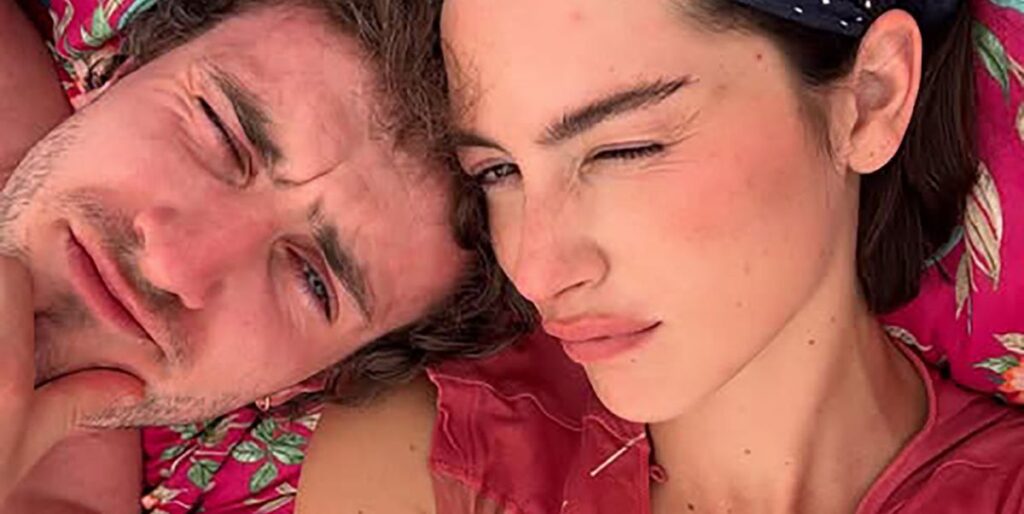
Meghan Trainor and Daryl Sabara Announce the Arrival of Daughter, Tricia: A Closer Look at Their Surrogacy Journey
Meghan Trainor and Daryl Sabara have officially expanded their family! The couple welcomed their third child, a daughter named Tricia, via surrogacy. This decision, while intensely personal, also shines a light on the increasing prevalence and acceptance of surrogacy as a family-building option, particularly within the celebrity sphere.
Strategic Family Planning: Understanding the Decision Behind Surrogacy
Choosing surrogacy is a multifaceted decision, often driven by a combination of medical, personal, and professional considerations. While Meghan Trainor and Daryl Sabara have not explicitly detailed the reasons behind their choice, it’s important to understand the common factors that lead individuals and couples to pursue this path. These factors can include:
- Medical Necessity: Certain medical conditions can make it difficult or impossible for a woman to carry a pregnancy to term. These conditions might involve uterine abnormalities, recurrent pregnancy loss, or serious health issues that could be exacerbated by pregnancy.
- Personal Preferences: Some individuals or couples may choose surrogacy due to personal preferences or concerns related to pregnancy and childbirth. This could stem from previous difficult pregnancies or a desire to avoid the physical demands of carrying a child.
- Career Considerations: For individuals with demanding careers, particularly in the entertainment industry, surrogacy can offer a way to expand their family without significantly disrupting their professional lives. This allows for a more controlled timeline and minimizes the physical toll on the intended mother.
It’s critical to approach the topic of surrogacy with sensitivity and respect for individual choices. The decision to pursue surrogacy is deeply personal, and the reasons behind it are often complex and nuanced. Understanding the various factors involved helps to foster a more informed and empathetic perspective on this family-building option.
The Growing Trend of Surrogacy Among Celebrities
Meghan Trainor and Daryl Sabara join a growing list of celebrities who have chosen surrogacy to build their families. This trend has helped to normalize and destigmatize the process, raising awareness and sparking conversations about reproductive options. Other notable celebrities who have utilized surrogacy include:
- Priyanka Chopra and Nick Jonas: Welcomed their daughter, Malti Marie, via surrogate in 2022.
- Kim Kardashian and Kanye West: Had two of their four children, Chicago and Psalm, via surrogate.
- Gabrielle Union and Dwyane Wade: Welcomed their daughter, Kaavia James, via surrogate in 2018.
- Anderson Cooper: Became a father to two sons, Wyatt and Sebastian, via surrogate.
The increasing visibility of surrogacy in the public eye has several significant implications. It provides a platform for open discussions about infertility, reproductive rights, and the diverse ways in which families can be formed. It also offers hope and encouragement to individuals and couples who are struggling with infertility or facing challenges in conceiving or carrying a pregnancy. However, it’s important to acknowledge that access to surrogacy remains unevenly distributed, with significant financial and legal barriers in many regions.
Understanding the Surrogacy Process: A Comprehensive Overview
Surrogacy is a complex and multifaceted process that involves legal, medical, and emotional considerations. There are two primary types of surrogacy:
- Gestational Surrogacy: This is the most common type of surrogacy. In gestational surrogacy, the surrogate carries a child that is biologically unrelated to her. The embryo is created through in vitro fertilization (IVF) using the intended mother’s egg and the intended father’s sperm, or through the use of donor eggs or sperm. The resulting embryo is then transferred to the surrogate’s uterus.
- Traditional Surrogacy: In traditional surrogacy, the surrogate is the biological mother of the child. She is artificially inseminated with the intended father’s sperm. This type of surrogacy is less common due to the complex legal and emotional issues that can arise.
The surrogacy process typically involves the following steps:
- Consultation and Evaluation: Intended parents meet with a fertility specialist and a surrogacy agency to discuss their options and undergo medical and psychological evaluations.
- Matching: The surrogacy agency matches the intended parents with a suitable surrogate. This process involves considering factors such as personality, values, and medical history.
- Legal Agreements: Legal contracts are drawn up to protect the rights and responsibilities of all parties involved, including the intended parents and the surrogate. These contracts address issues such as parental rights, financial compensation, and medical decision-making.
- Medical Procedures: The intended mother (or egg donor) undergoes ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval. The eggs are then fertilized with the intended father’s (or sperm donor’s) sperm in a laboratory. The resulting embryo is transferred to the surrogate’s uterus.
- Pregnancy and Delivery: The surrogate carries the pregnancy to term and delivers the baby. The intended parents are typically present for the birth and take custody of the child immediately after delivery.
The cost of surrogacy can vary widely depending on factors such as the type of surrogacy, the location, and the agency fees. It’s essential for intended parents to carefully research and understand all the financial implications before embarking on the surrogacy journey.
The Ethical and Legal Landscape of Surrogacy
Surrogacy raises a number of ethical and legal considerations. These considerations vary significantly across different jurisdictions, creating a complex and often confusing landscape. Some of the key ethical and legal issues include:
- Parental Rights: Determining the legal parents of a child born through surrogacy can be complex, particularly in cases involving international surrogacy or same-sex couples. Laws regarding parental rights vary widely, and it’s crucial to establish legal parentage before the child is born.
- Compensation: The issue of compensating surrogates is a contentious one. Some argue that surrogates should be compensated for their time, effort, and the physical demands of pregnancy, while others believe that surrogacy should be altruistic. Laws regarding compensation vary, with some jurisdictions prohibiting commercial surrogacy.
- Exploitation: There are concerns about the potential for exploitation of surrogates, particularly in developing countries. It’s essential to ensure that surrogates are treated with respect and dignity and that they are fully informed about the risks and benefits of surrogacy.
- Informed Consent: All parties involved in surrogacy must provide informed consent. This means that they must understand the risks and benefits of surrogacy, as well as their legal rights and responsibilities.
The legal and ethical landscape of surrogacy is constantly evolving. It’s crucial for intended parents and surrogates to seek legal advice and to stay informed about the laws and regulations in their jurisdiction.
Infertility: A Growing Global Concern
The decision to pursue surrogacy is often linked to infertility, a growing global health concern affecting millions of people worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), infertility affects millions of people of reproductive age worldwide and impacts their families and communities. Estimates suggest that between 48 million couples and 186 million individuals globally live with infertility. Infertility rates vary across regions and are influenced by a range of factors, including:
- Age: Female fertility declines significantly with age, particularly after the age of 35.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can negatively impact fertility in both men and women.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and sexually transmitted infections (STIs), can contribute to infertility.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environmental toxins can also affect fertility.
Addressing infertility requires a multifaceted approach, including prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Prevention efforts should focus on promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing STIs. Diagnosis involves a thorough evaluation of both partners to identify the underlying cause of infertility. Treatment options range from lifestyle modifications and medication to assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as IVF and surrogacy. Access to affordable and effective infertility treatment remains a significant challenge in many parts of the world.
The Role of Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) play a crucial role in helping individuals and couples overcome infertility and build their families. ART encompasses a range of techniques, including:
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF involves retrieving eggs from a woman’s ovaries and fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the woman’s uterus.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): IUI involves placing sperm directly into a woman’s uterus, increasing the chances of fertilization.
- Egg Donation: Egg donation involves using eggs from a donor to create embryos through IVF. This option is often used by women who have diminished ovarian reserve or who are at risk of passing on genetic disorders.
- Sperm Donation: Sperm donation involves using sperm from a donor to fertilize a woman’s egg. This option is often used by single women or couples where the male partner has severe male factor infertility.
- Surrogacy: As discussed earlier, surrogacy involves a woman carrying a pregnancy for another individual or couple.
ART has revolutionized the treatment of infertility, offering hope to millions of people who would otherwise be unable to conceive. However, ART is not without its challenges. It can be expensive, time-consuming, and emotionally demanding. It’s important for individuals and couples considering ART to carefully weigh the risks and benefits and to seek support from qualified medical professionals and counselors.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Family Building
The methods by which individuals and couples build their families are constantly evolving. As societal attitudes shift and technology advances, we can expect to see further changes in the landscape of family building. Some of the key trends to watch include:
- Increased Acceptance of Diverse Family Structures: There is a growing acceptance of diverse family structures, including single-parent families, same-sex parent families, and families formed through adoption and surrogacy.
- Advancements in Reproductive Technology: Continued advancements in reproductive technology are likely to improve the success rates of ART and to expand the options available to individuals and couples facing infertility.
- Greater Access to Fertility Treatment: Efforts are underway to increase access to affordable and effective fertility treatment, particularly in underserved communities.
- More Open Conversations About Infertility: Open and honest conversations about infertility are helping to reduce stigma and to encourage individuals to seek help.
Meghan Trainor and Daryl Sabara’s decision to use surrogacy to welcome their daughter, Tricia, is a testament to the evolving landscape of family building. By sharing their story, they are helping to normalize surrogacy and to inspire others who are facing challenges in conceiving or carrying a pregnancy. As we move forward, it’s crucial to continue to promote understanding, empathy, and support for all individuals and couples who are striving to build their families.
FAQ: Surrogacy and Family Planning
What is surrogacy?
Surrogacy is an arrangement in which a woman carries and delivers a child for another person or couple (the intended parents). It’s typically used when the intended mother is unable to carry a pregnancy to term or when a same-sex male couple wants to have a child.
What are the different types of surrogacy?
There are two main types of surrogacy: gestational surrogacy and traditional surrogacy. In gestational surrogacy, the surrogate carries a child that is biologically unrelated to her (the egg and sperm come from the intended parents or donors). In traditional surrogacy, the surrogate is also the biological mother of the child (her egg is used). Gestational surrogacy is more common due to legal and ethical considerations.
What are the legal considerations of surrogacy?
Surrogacy laws vary widely from state to state and country to country. It’s crucial to consult with a lawyer specializing in reproductive law to understand the legal requirements and ensure that the intended parents’ rights are protected. Legal issues typically involve establishing parental rights, drafting surrogacy agreements, and navigating birth certificate procedures.
What are the ethical considerations of surrogacy?
Ethical considerations surrounding surrogacy include concerns about the potential exploitation of surrogates, the commodification of children, and the impact on the surrogate’s physical and emotional well-being. It’s important to ensure that surrogates are fully informed about the risks and benefits of surrogacy and that they are treated with respect and dignity.
How much does surrogacy cost?
The cost of surrogacy can vary widely, depending on factors such as the type of surrogacy, the location, the agency fees, and the medical expenses. It can range from $100,000 to $200,000 or more. Intended parents should carefully research and understand all the financial implications before embarking on the surrogacy journey.
What are the alternatives to surrogacy?
Alternatives to surrogacy include adoption, using donor eggs or sperm, and focusing on other aspects of life besides parenthood. The best option depends on the individual’s or couple’s circumstances and preferences.
How do I find a surrogacy agency?
You can find a surrogacy agency by searching online, asking for referrals from fertility clinics, or contacting organizations that specialize in reproductive assistance. It’s important to choose an agency that is reputable, experienced, and committed to ethical practices.
What is IVF, and how does it relate to surrogacy?
IVF (in vitro fertilization) is a process in which eggs are retrieved from a woman’s ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the woman’s uterus (or, in the case of surrogacy, the surrogate’s uterus). IVF is often used in conjunction with surrogacy, particularly gestational surrogacy, to create the embryos that the surrogate will carry.
What are the risks of surrogacy for the surrogate?
The risks of surrogacy for the surrogate are similar to those of any pregnancy, including the risks of carrying multiples, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and postpartum depression. There are also emotional risks associated with carrying a child for someone else and relinquishing the baby after birth.
What are the benefits of surrogacy for intended parents?
The benefits of surrogacy for intended parents include the opportunity to have a child who is genetically related to them (in the case of using their own eggs and sperm), the ability to be involved in the pregnancy process, and the joy of becoming parents.